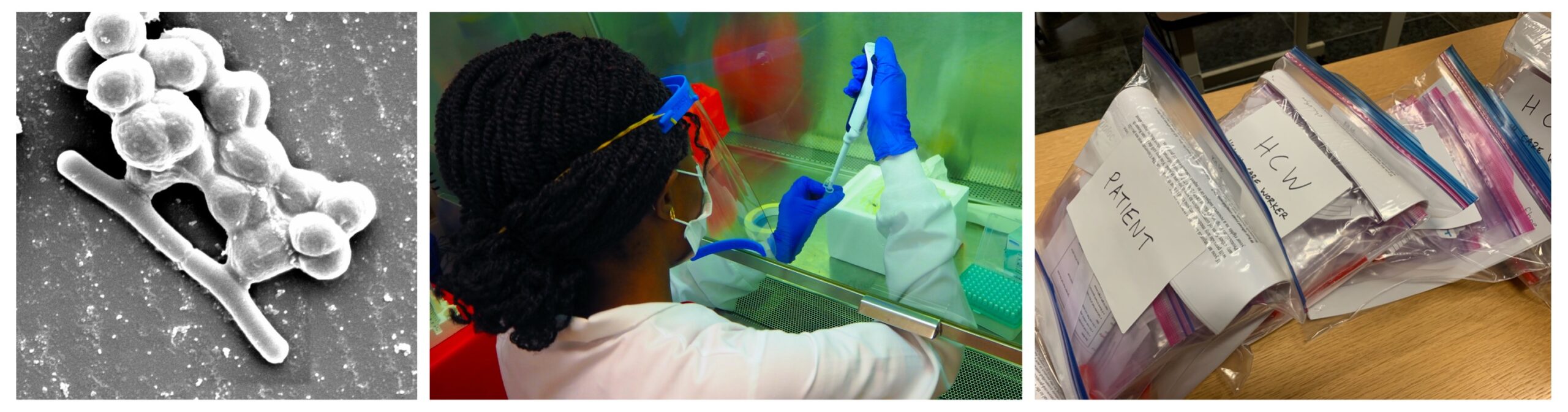
The Human Microbiome in Nutrition, Disease, and Mental Health
The human microbiota consists of approximately 40 trillion microorganisms, and the genes of these taxa vastly outnumber those found in the human genome. These microbes influence our health in a variety of ways, including training the immune system to respond to infection and affecting reproductive health outcomes (such as those associated with preterm birth and postpartum depression). These outcomes can be moderated by lifestyle and individual factors, such as diet and physiology. Diet can influence the diversity and metabolic behavior of the microbiome, as dietary components act as substrates for microbial metabolism, and the gut-brain axis further mediates the interaction between bacterial communities in the intestine and neurological, immunological and endocrinological processes. We continue to explore the intricate relationship between our microbiota and our health through clinical-based research at the UCSD School of Medicine and with collaborators around the world.

Recent and ongoing projects:
- Airway microbiome and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Profiling airway microbe–host interactions in COPD through an in-depth analysis of the sputum metagenome, metabolome, host transcriptome and proteome of COPD patients and healthy individuals. Publication: Multi-omics analyses of airway host–microbe interactions in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease identify potential therapeutic interventions
- Characterizing the molecular interaction between Rothia bacteria and SARS-CoV-2: Building upon our previous hospital study to identify the mechanisms by which the viral spike protein binds more efficiently to bacteria from the Rothia genus compared to other bacterial taxa.
- Colonoscopy, lavage, and precision nutrition: In a groundbreaking study, we are exploring how diet choices post colonoscopy can increase or decrease the risk of colonic polyp emergence and therefore the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Fecal microbiome transplants: Understanding microbial interactions that shape ecological stability of transplants.
- Gender-affirming hormone replacement therapy and gut and vaginal microbiomes: Characterization of the effects of testosterone therapy initiation on the gut and vaginal microbiomes of transgender men.
- Gut-brain axis: Impact of fecal microbiota transplantation and probiotic administration on microbial GABA metabolism as a treatment for depression and anxiety. Publication: Effects of ‘Healthy’ Fecal Microbiota Transplantation against the Deterioration of Depression in Fawn-Hooded Rats
- HPV and the microbiome: Role of the cervicovaginal microbiome in moderating Human Papillomavirus disease severity in women in Puerto Rico. Publication: The cervical microbiota of Hispanics living in Puerto Rico is nonoptimal regardless of HPV status
- Kombucha supplementation to a western diet: Impact of fermented foods on microbiome, inflammation, and host health.
- METS: Role of diet and lifestyle differences across countries in shaping gut microbial communities and metabolism in adults of African descent. Publication: Gut microbiota and fecal short chain fatty acids differ with adiposity and country of origin: The METS-Microbiome Study
- Mycobiome and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Investigating the gut mycobiome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, from patients with and without NAFLD.
- Outdoor exposure in childhood: Longitudinal characterization of gut microbiomes and health markers in children enrolled in outdoor preschool.
- Precision nutrition: The Microbiome and Metagenomics Center at UC San Diego is part of the Nutrition for Precision Health consortium, which is powered by the NIH’s All of Us Research Program.
- Preterm infant microbiome and metabolome: Influence of microbial metabolism on asthma risk in preterm infants, and impact of breastfeeding on the preterm infant microbiome and metabolome. Publication: The impact of maternal asthma on the preterm infants’ gut metabolome and microbiome (MAP study)
- Protein restriction and fiber supplementation: The role of gut microbiome in host nutritional and metabolic adaptation during low dietary protein conditions. Publication: Gut microbiota mediate the FGF21 adaptive stress response to chronic dietary protein-restriction in mice
- Skin microbiome: Measuring skin attributes in peri- and post-menopausal women and identifying associations with the skin microbiome in rural vs urban demographics.
- Reviews and Commentaries
Microbial Ecology of the Built Environment
Urbanization and our indoor lifestyle have deeply affected how we acquire and interact with our microbiota. In the Gilbert Lab, we are working to answer fundamental questions about how built environments shape our microbial interactions, including what factors influence their assemblage, persistence, selection for genetic traits, and transmission throughout these spaces. Much of our research relies on longitudinal surveys. This includes our Home Microbiome Project, in which we recruited public scientists to collect microbes from their home and skin over time. Additionally, our Hospital Microbiome Project characterized microbes from hospital patients, staff, and surfaces over the course of its first year, post-opening. During the COVID-19 pandemic, we followed up on this study to examine the influence of COVID-19 patient occupancy on hospital surface microbiomes, and we continue to explore ways in which we can manipulate microbial communities to reduce infection risk indoors, such as in hospitals, in homes, and on the International Space Station.
Recent and ongoing projects:
- Biologically active building materials: Combining biological control with 3D printing to engineer living surfaces, while also examining the ethical, legal, and social implications of this approach. This project is also part of the Research Experience and Mentoring (REM) program through the National Science Foundation.
- Biological control on surfaces: Using biologically active cleaning products to reduce pathogen abundance, antibiotic resistance, and virulence in the built environment.
- COVID-19 hospital study: Tracking SARS-CoV-2 and associated microbes through space and time. Publication: SARS-CoV-2 detection status associates with bacterial community composition in patients and the hospital environment
- Hospital interventions: Quantification and reduction of antibiotic resistance in hospitals by determining selection pressures that shape emergence and tracking the routes of transmission.
- NASA Microbial Tracking-3: Understanding the emergence and persistence of pathogenesis and antibiotic resistance on the International Space Station.
- Soil seeding in homes: Tracking how indoor bacterial and fungal communities are shaped by adding forest soil into homes with varying occupancy and levels of interaction with the outdoors.
- Yoga mat microbiome: Quantifying the dose-dependent impact of yoga mat colonization on the microbiology of the built environment and assessing spread of microbes from yoga mats to the surrounding built environment.
- Reviews:
- Microbial Exchange via Fomites and Implications for Human Health
- Microbiology of the Built Environment
- Embracing Healthy Microbiomes, Including Access to Nature and Pets
- Microbiology of the built environment: harnessing human-associated built environment research to inform the study and design of animal nests and enclosures
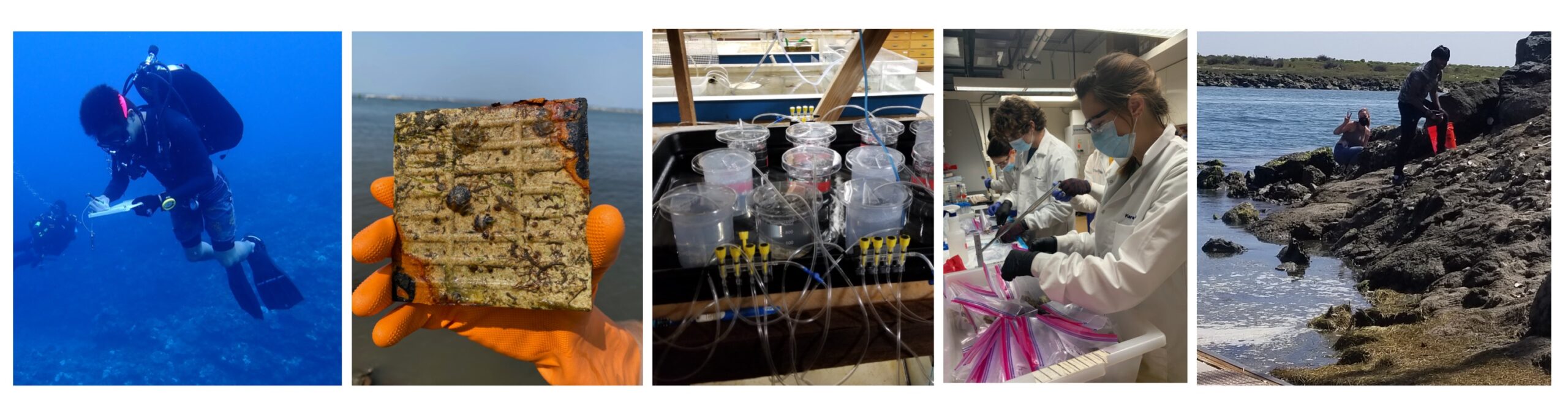
Marine Microbial Ecology in Human and Environmental Health
The links between ocean and human health are of great interest to our group, and we are particularly interested in understanding how host-microbe interactions present opportunities to ameliorate anthropogenic impacts and how host-associated microbiomes influence disease ecology. At Scripps Institution of Oceanography, we have a diverse set of research objectives designed to address urgent issues in environmental and human health linked to our oceans.

Microbial ecology, evolution, and biogeography over time:
- DDT pollution and microbial bioremediation: DDT and associated chemicals such as DDMU, DDNU, DDE, DDT, etc. (DDT+) are absorbed onto marine sediment and accumulate in invertebrates, which threatens the marine food web, human and environmental health. Our objective is to determine how DDT biodegradation by defined bacterial consortia could influence DDT and associated breakdown product accumulation in model invertebrates. We are working with a team of SIO scientists to investigate these dynamics at an offshore dumpsite in southern California.
- Time series investigation of human impacts on riverine communities: In conjunction with scientists at Argonne National Laboratory and the Metropolitan Wastewater Reclamation District of Greater Chicago (MWRD), we assessed the response of microbial communities in an urban waterway before and after wastewater treatment infrastructure upgrades. Publication: Microbiome response in an urban river system is dominated by seasonality over wastewater treatment upgrades
- Review: Conceptual strategies for characterizing interactions in microbial communities
Host-microbe-environment interactions:
- Coral reef ecology and disease: Mapping coral microbiomes across species and geography and associated changes in coral health.
- Fecal microbiota transplants in dolphins: Tracking engraftment and efficacy of fecal microbiota transplants for dolphins with IBS.
- Mangrove microbiome and restoration: Investigating the role of the mangrove microbiome for salinity tolerance. We are also leaders in the Mangrove Microbiome Initiative. Perspective: Introducing the Mangrove Microbiome Initiative: Identifying Microbial Research Priorities and Approaches To Better Understand, Protect, and Rehabilitate Mangrove Ecosystems
- Oyster microbiome and coastal pollution: Exploring whether exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) influences oyster health and the oyster microbiome, and whether oyster-associated microbes degrade these pollutants.
Disease ecology in a changing climate:
- Coastal human bacterial pathogens: Enumerating Vibrio spp in water and shellfish in the context of microbiomes, quantifying the vector potential of microplastics for foodborne pathogens. Publication: Host and Water Microbiota are Differentially Linked to Potential Human Pathogen Accumulation in Oysters
- Shellfish pathogens: Quantifying host and microbial responses to pathogen exposure under different temperature conditions (CaXc causing Abalone Withering Syndrome, OsHV-1 initiating Pacific Oyster Mortality Syndrome), and characterizing response of oyster microbiomes to differing environments. Publication: Variation in Survival and Gut Microbiome Composition of Hatchery-Grown Native Oysters at Various Locations within the Puget Sound